
Dalton Transactions
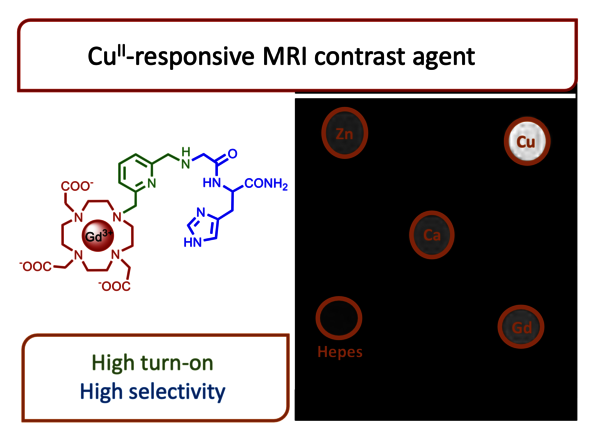
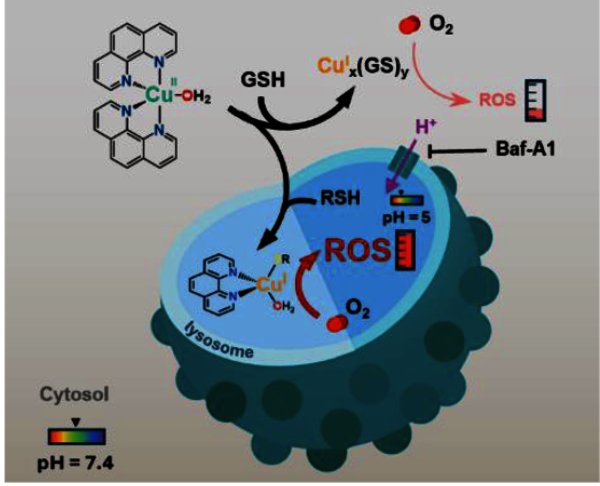
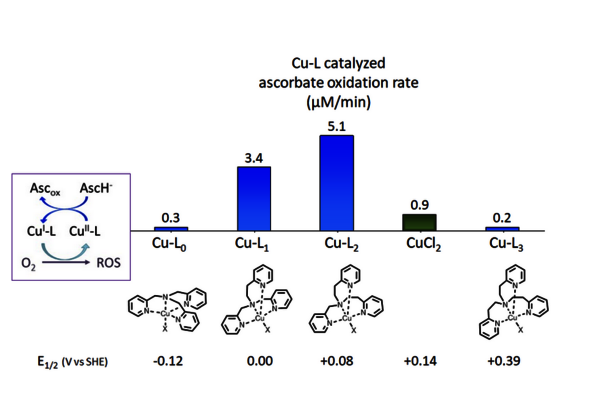
Abstract In the pursuit of CuII-responsive MRI contrast agents with enhanced CuII affinity, we report the synthesis and characterization of two LnIII-DO3A-C3AmpicGH complexes (LnIII = GdIII, EuIII), featuring a tetradentate CuII-binding moiety, along with the corresponding mononuclear CuII-C3AmpicG…













![[Translate to English:]](/websites/_processed_/0/4/csm_signature-unistra_fee3442f1d.png)
![[Translate to English:]](/websites/_processed_/0/e/csm_logo-cnrs_c0f610620b.png)
![[Translate to English:]](/websites/_processed_/9/4/csm_logo-fondation-lehn_24043a5484.png)