Abstract
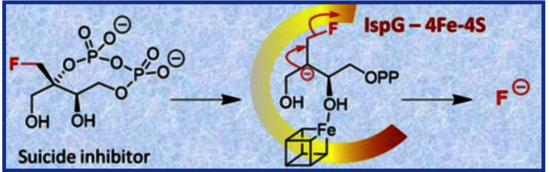
IspG (also known as GcpE) is a key [4Fe-4S] metalloenzyme that catalyzes the penultimate step of the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway, a well-established target for the development of new antimicrobials. This oxygen-sensitive enzyme mediates the reductive dehydroxylation of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) to (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate (HMBPP), requiring electron transfer proteins to deliver two electrons needed for catalysis. To probe the mechanism of IspG and access new mechanism-based inhibitors, we synthesized a substrate analogue, monofluoromethyl-d-erythritol cyclodiphosphate, in which the natural methyl group of MEcPP is replaced by a CH2F group. This analogue proved to be a potent inhibitor of IspG. This study also demonstrates that electron capture is a prerequisite for inhibition and that the inhibitor leads to fluoride release in the IspG-catalyzed reaction. Together, these results provide further support for the involvement of a carbanionic intermediate in the IspG mechanism.
Graphical Abstract
The fluoromethyl analogue of MEcPP was identified as a very potent inhibitor of the oxygen-sensitive [4Fe-4S] metalloenzyme IspG. In the course of the IspG-catalyzed transformation, this novel compound undergoes fluoride elimination, offering additional evidence for the involvement of a carbanionic intermediate in the mechanism of this enzyme.