Abstract
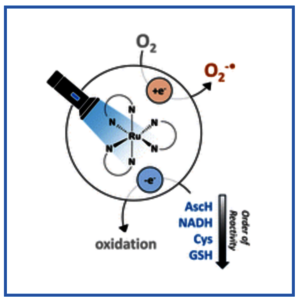
Ru complexes are widely studied in photodynamic therapy. The type I mechanism of action is based on a photoinduced electron transfer from the complex to O2 and needs an electron donor to be catalytic. Little is known about electron donors among physiologically relevant compounds. Hence, we investigated the oxidation of ascorbate, NADH, cysteine, and glutathione with the canonical [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2 as well as a derivative with a peripheral disulphide unit, [Ru(S–Sbpy)(bpy)2](PF6)2. The established reactivity order is ascorbate > NADH ∼ cysteine > glutathione.