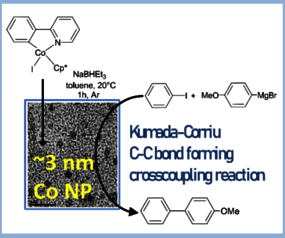
Abstract
This study shows that the nanoparticles produced by the reductive
decomposition of a cobalt (+III) metallacycle derived from 2-phenylpyridine upon
treatment with the highly nucleophilic Na[Et3BH] are capable of promoting the Kumada-
Corriu cross coupling of aryl halides with aryl-bromomagnesium compounds (Grignard
reagents) in various conditions and in the presence of various stabilizing ligands to afford
the non-symmetric organic bisaryl product in reasonable yields. This study provides
further evidence that incidental Co nanoparticles possess a reasonable capability in
homogeneous catalysis, thereby complementing a prior report on their ability to promote
the hydrosilylation of unsaturated organic substrates, such as nitriles. Co nanoparticles
were characterized by HRTEM, EDX, EELS, and SAED techniques. TEM analyses
revealed that the nanoparticles were uniformly spherical in shape, with a narrow size
distribution; no nanoparticles larger than 3 nm were observed. EDX analysis displaying
a characteristic Co signature at about 7 keV. The magnetic behavior of the nanoparticles
studied by SQUID analysis in toluene using a temperature varied from 2 to 300 K, and a
low magnetic field (10-3T) in ZFC-FC conditions.
Reference
Kumada-Corriu Cross-Coupling Reaction Catalyzed by Cobalt Nanoparticles Arising from the Reductive Decomposition of a Cobaltacycle
Masoumeh Behzadi, Mélanie Boucher, Jérôme Robert & Jean-Pierre Djukic
An-Najah University Journal for Research - A (Natural Sciences), Availabe online 2025-09-02 – DOI: 10.35552/anujr.a.39.3.2583
Contact
Jean-Pierre Djukic (team LCSOM), Institut de Chimie de Strasbourg, UMR 7177.